Mark Abrams
Mark heads up the trade finance offering at TFG where his team focuses on bringing in alternative structured finance to international trading companies.
Access trade, receivables and supply chain finance
We assist companies to access trade and receivables finance through our relationships with 270+ banks, funds and alternative finance houses.
Get Started
Download our our free Letters of Credit guide

Download

ADVERTISEMENT
Contents
Navigating MT 765: The role of guarantee/standby letter of credit demand in global trade
Swift message type (MT) 765 helps ensure efficient and secure interbank communication in trade finance.
This protocol, which focuses on guarantee and standby letter of credit demands, enables stakeholders to demand payment confidently under specific financial instruments.
To understand MT 765, it is important to examine its operational specifics and evolution in the world of trade finance technology.
Overview of MT 765
MT 765 enables the request for payment under guarantees or standby letters of credit.
It is a direct line of communication from the beneficiary (or their representative) to the guarantee issuer. This role helps activate the financial commitments outlined in trade finance instruments, such as documentary credits and standby letters of credit.
MT 765 enhances the security and reliability of international trade transactions by enabling beneficiaries to use these financial tools effectively once the payment conditions are satisfied.
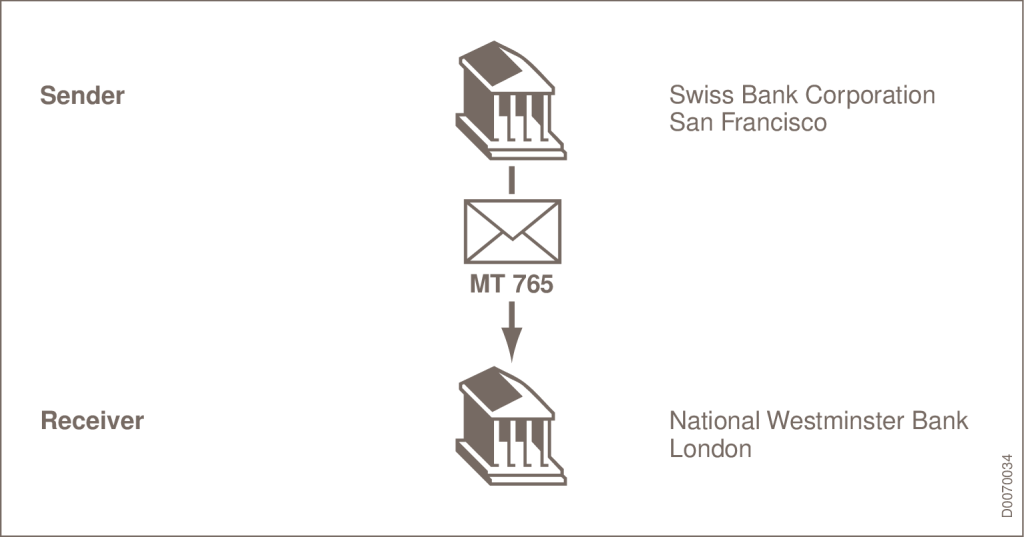
SOURCE: SWIFT
Important key fields
MT 765 has several key fields, including:
- Field 20 (Transaction Reference Number): This field provides a unique identifier for each demand, enabling precise tracking and reference.
- Fields 32B (Demand Amount) and 22G (Demand Type): These fields specify the amount being demanded and the nature of the demand, which are critical for ensuring the clarity and validity of the payment request.
- Fields 52A (Issuer) and 59A (Beneficiary): Identify the parties involved, ensuring that demands are accurately directed and attributed.
- Field 31L (Date of Demand): Marks the formal request’s timing, crucial for adherence to the terms under which the guarantee or standby letter of credit was issued.
Users and purpose
MT 765 primarily serves beneficiaries of guarantees or standby letters of credit. This includes companies and financial institutions engaged in international trade.
Its core purpose is to enforce financial commitments through official payment requests, vital for managing risks, resolving disputes, and ensuring compliance with regulations.
Role of MT 765 in trade finance
MT 765 ensures the smooth operation of trade finance transactions as it helps with risk management and dispute resolution.
By enforcing contractual commitments within trade instruments, MT 765 introduces a standardised approach for invoking guarantees or standby letters of credit. This standardisation is key to building trust and promoting efficiency across international trade channels.
Impact on international trade
MT 765 introduces a formalised process for payment requests, ensuring that financial guarantees fulfil their role as reliable instruments in trade.
This capability of MT 765 addresses the challenges of payment risks and disputes, enhancing the predictability and reliability of trade finance.
Consequently, MT 765 has become an indispensable asset within the global trading ecosystem.
Technological advances and what lies ahead
Digitalisation and blockchain technology have the potential to revolutionise the use of MT 765. These technologies aim to streamline the demand process, reduce errors, and enhance transaction security.
Experts anticipate that the years ahead will see a deeper integration of MT 765 with digital trade platforms.
This evolution prepares MT 765 to navigate new challenges and capitalise on opportunities presented by technological advancements.
As the trade finance sector evolves, influenced by globalisation and technological advances, the importance of understanding and applying MT 765 remains essential for confidently navigating the future complexities of international trade.